
Triangle DEF is formed by reflecting ABC across the y-axis and has vertices D (4, -6), E (6, -2) and F (2, -4). Algebraically, the ordered pair (x, y) becomes (-x, y). In a reflection about the y-axis, the y-coordinates stay the same while the x-coordinates take on their opposite sign. All of the points on triangle ABC undergo the same change to form DEF. Triangle DEF is formed by reflecting ABC across the x-axis and has vertices D (-6, -2), E (-4, -6) and F (-2, -4). Algebraically, the ordered pair (x, y) becomes (x, -y). In a reflection about the x-axis, the x-coordinates stay the same while the y-coordinates take on their opposite signs. The most common cases use the x-axis, y-axis, and the line y = x as the line of reflection. There are a number of different types of reflections in the coordinate plane. This is true for any corresponding points on the two triangles and this same concept applies to all 2D shapes. A, B, and C are the same distance from the line of reflection as their corresponding points, D, E, and F. The figure below shows the reflection of triangle ABC across the line of reflection (vertical line shown in blue) to form triangle DEF.

The same is true for a 3D object across a plane of refection.
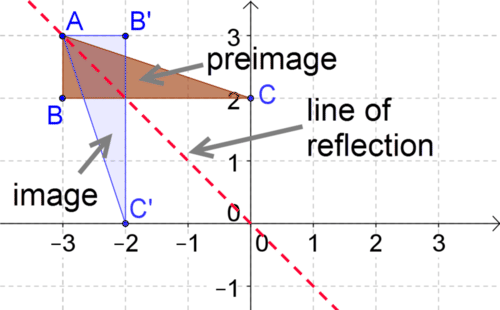
In a reflection of a 2D object, each point on the preimage moves the same distance across the line of reflection to form a mirror image of itself. The term "preimage" is used to describe a geometric figure before it has been transformed "image" is used to describe it after it has been transformed. When an object is reflected across a line (or plane) of reflection, the size and shape of the object does not change, only its configuration the objects are therefore congruent before and after the transformation. In geometry, a reflection is a rigid transformation in which an object is mirrored across a line or plane. Home / geometry / transformation / reflection ReflectionĪ reflection is a type of geometric transformation in which a shape is flipped over a line.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
